
With an estimated population of 17.8 million, Zambia is a politically stable multi-party democracy, rich in natural resources. The country has experienced two decades of positive economic growth and a corresponding expansion of middle-class income. Zambia saw a 3.5 % contraction in GDP in 2020 owing to a combination of unsustainable government debt, a series of droughts affecting agricultural production, a deficit in power generation and knock-on effects from the global coronavirus pandemic. Despite these downturns, the economy is expected to grow by 0.6% by the year-end of 2021
There are several promising commercial opportunities in Zambia’s emerging economy, most notably in;
The Zambian economy enjoys liberalized prices on most goods/services and does not have currency controls. As a result, this has created a suitable environment for Import-Export Trade with other counties.
Zambia’s major export destinations are Switzerland, China, Singapore, the Democratic Republic of Congo, South Africa, Luxembourg and Zimbabwe. The major destinations earnings totalled US$2.8 billion in the third quarter of 2021, which is 24.5% higher than 2020. Copper exports grew by 23.6% to US$2.1 billion owing to favourable prices that offset a 19.0% fall in export volumes. The average realised copper prices rose by 52.4% to US$9,681.8 per tonne compared to US$6,352.5 a year ago. Higher demand for copper, particularly from China, explained this outturn. Chart 1 and Table 1 shows export earnings from the main destinations.
Zambia’s other export commodities include lime, cement, iron and steel, pearls, precious stones and metals; as well as nuclear reactors, boilers, and mechanical appliances.
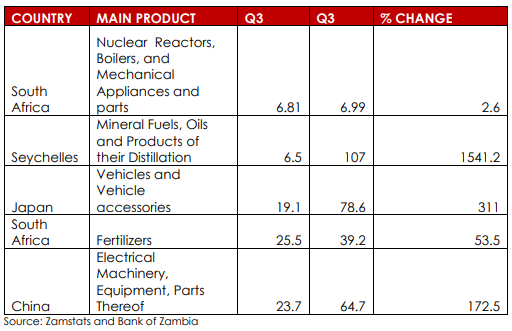
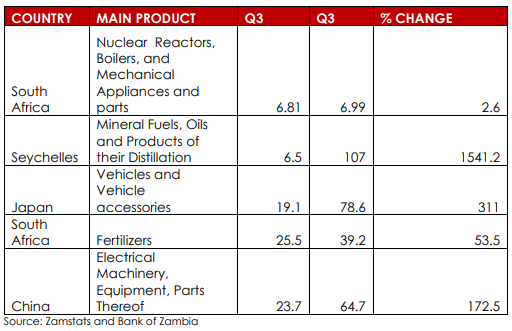
Zambia’s major import destinations are; South Africa, China, United Arab Emirates, India, Democratic Republic of Congo, Seychelles and Japan (replaced the UK). The value of merchandise imports was 57.9% higher, at US$2.14 billion in the third quarter of 2021 than in 2020. Imports from the top five source countries accounted for 77.3% of total imports with South Africa being the largest contributor at 28.6%. The increase was broadly-based on an uptick in domestic activity, appreciation of the Kwacha and the continued easing of supply constraints in trading partner countries( especially by China and South Africa), which accounted for the increase in imports.
The United States is another import-export partner among Zambia’s trade partners. In $71.8 million worth of commodities were imported into the country, this is down 38% from the $99.3 million imported in 2019. The imports consisted primarily of machinery, rubber, and vehicles. In 2020 Zambia exported $40.3 million in commodities to the United States which consisted almost entirely of; Copper, Cobalt, Precious stones (primarily emeralds), and Cotton. To promote trade in the region the United States has signed a trade and investment framework agreement with the Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) to boost trade relations with the United States and among COMESA member states.
UBA Zambia is well-positioned to facilitate and support trade in Zambia, through our robust and world-class service offerings that include credit facilities, digital payment solutions, FX and remittances.